Radiation Harmful Effects on Environment/ Antivirus
Biological Effects of Radiation
What do we mean by safety?
The word "security" has different meanings depending on the person. For many, safety is synonymous with the absence of risks or dangers. But the reality is, there is always some level of risk in pretty much anything we do.For example, speed limits on roads are set to optimize the safety of road users. This does not prevent accidents, however, even if motorists obey the speed limits. Despite these risks, we still make a conscious decision to drive.The same conscious decisions are made with respect to radiation. Exposure to radiation poses a health risk. Knowledge of these risks allows the CNSC and other regulators to set dose limits and formulate regulations that limit exposure to an acceptable or tolerable risk (some may even use the phrase "limit of safety ”).
How does radiation affect cells?
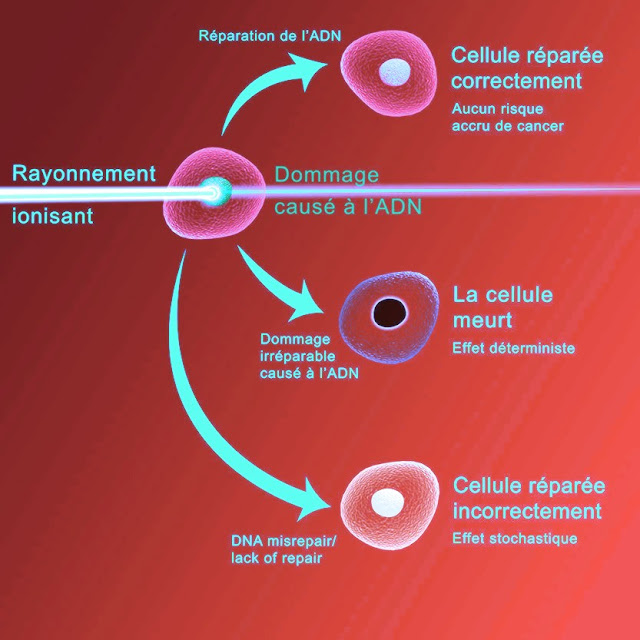
The alteration or breakdown of DNA molecules is the primary health effect of radiation. DNA, made up of two long chains of nucleotides coiled around each other in a double helix, is the molecular compound in the nucleus of a cell that defines its structure and function. Radiation can alter this chain. In this case, three phenomena can occur:
DNA repairs itself properly
In this case, the cell is correctly repaired and continues to function normally. The DNA molecule is permanently damaged, every second of the day, and cells have a natural ability to repair these damage.
The DNA damage is too severe and the cell dies ( deterministic effects )
If the DNA or other essential parts of the cell receive a large dose of radiation, the cell can either die or be damaged to the point where it cannot repair itself. If this phenomenon affects a large number of cells in a tissue or organ, the early effects of radiation may occur. These are deterministic effects whose severity varies according to the radiation dose received. They can result in burns, cataracts and, in extreme cases, death.
The first evidence for the deterministic effects of radiation was seen in early researchers and users of radiation. They presented severe damage to the skin and hands due to exposure to an excessive dose of radiation. More recently, the same phenomena were observed after the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in 1986, during which more than 130 workers and firefighters received high doses of radiation (800 to 16,000 mSv) and presented by following radiation sickness. Two of the people exposed died a few days after the exposure. More than 30 workers and firefighters died in the three months following the accident.
The CNSC and other international regulatory bodies have measures, including very strict dose limits and databases for tracking radioactive sources, to mitigate risks that may pose to members of the public or exposed workers. at doses of radiation high enough to cause deterministic effects. The CNSC also has very strict regulations for the handling of nuclear substances and devices in Canada.
The cell repairs itself poorly, but continues to live ( stochastic effects )
In some cases, the DNA of the cell can be damaged by radiation without the damage in question causing the death of the cell. This can continue to live and even reproduce itself, but the cell and its descendants can no longer function properly and even disrupt the functioning of other cells. The probability of this type of adverse reaction is proportional to the dose and is called the stochastic effect - when there is a statistical probability that the exposure will induce effects. In this case, the probability is proportional to the dose. However, when the effects will occur and their severity are independent of the dose.This process concerns each of us at all times. In fact, we are exposed to about 15,000 such events every second. Sometimes the structure of the cell changes because it repairs itself poorly. This alteration may have no effect or the effect in question may appear later in life. Cancer or hereditary effects may or may not occur.
Epidemiological evidence
Studies of survivors of atomic explosions in Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945 indicate that radiation exposure had the main effect of increasing the incidence of cancer and leukemia.
Comparable results were observed:
in people who have received radiation therapy or had a diagnostic test involving radiation;
among former uranium miners;
among workers who made atomic weapons;
in people exposed to radiation as a result of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant;
in people exposed to radon in their homes.
Studies have shown that radiation exposure increases the frequency of certain cancers that already occur spontaneously in the population and that this increase is proportional to the radiation dose. In other words, the higher the dose, the higher the risk of cancer. However, studies to date have not demonstrated the onset of an excessive number of cancers or other diseases in people chronically exposed to radiation at doses below about 100 mSv. (The lowest dose causing an excess number of cancers in atomic explosion survivors was in the order of 80 mSv.) antivirus.
Hereditary radiation-induced effects
Genetic damage occurs when the DNA of sperm or egg cells is damaged. This causes the emergence of an anomaly which is passed down from generation to generation. According to studies conducted on animals, such as fruit flies by Hermann J. Muller in 1926, exposure to radiation causes genetic mutations. However, to date, no known genetic effects have been observed in humans following exposure to radiation. These are studies which also covered 30,000 children of survivors of the atomic bombings on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan in 1945 (BEIR VII, UNSCEAR Report 2001).



Comments
Post a Comment